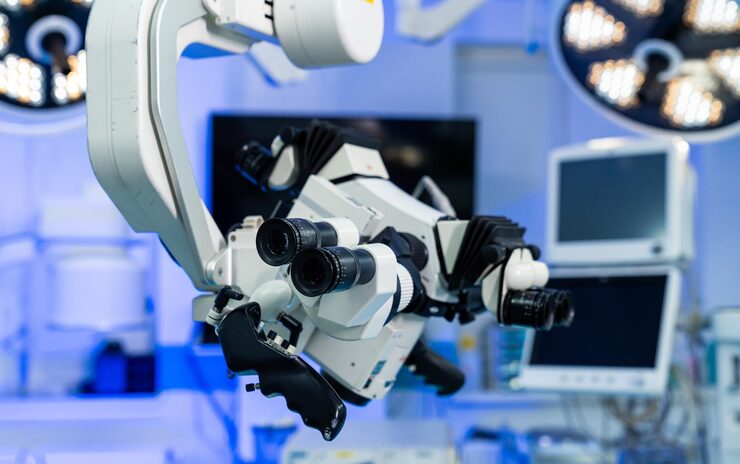
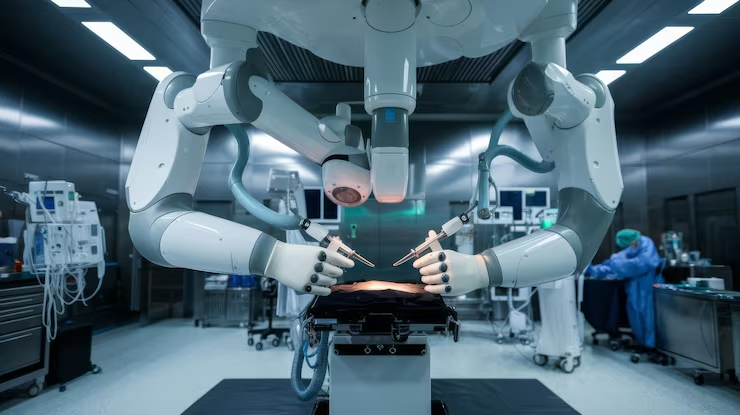
Canadian healthcare is increasingly focused on providing access regardless of geographic barriers. Tele-surgery and remote procedures are driving this shift, meaning that specialized medical skills are no longer limited to large cities. Robendy’s advanced surgical robot, known for its precision and control, leads this innovation. The technology enables surgeons equipped with this tool to perform complex surgeries remotely, expanding access to advanced surgical services across the country.
Bridging the Distance with Robendy’s Technology
It has become a reality that a surgeon is now able to operate miles away. The system of Robendy is one of the main parts of this technological movement, which enables control and provides feedback in real time. This helps the hospitals in remote places to tap into specialists who may not be employees. The system is designed to be user-friendly for both the surgeon and the assisting team, making the process seamless. It is a powerful new tool in modern medicine.
Expanding Access to Specialized Expertise
The capability to perform tele-surgery and remote operation directly addresses the challenge of healthcare inequality in remote regions. Specialized surgeons can now consult on or perform procedures in a distant hospital without the need for travel. This aspect helps to minimize critical care delays to a large extent. It also makes sure that whenever a patient is admitted to any region of Canada, they are exposed to the highest quality of surgical expertise. Nursing technology is a significant leap towards equity in healthcare.
The Role of Robotic Precision
Robendy’s high-precision, high-control surgical robot is an essential tool for remote procedures. The movements of the robot are constant and accurate, even when it is being operated somewhere far. This stability removes any possible latency or lag problems that may occur on a traditional remote-control system. Its hi-tech surgical equipment ensures that all the movements are correct and precise. The system provides a reliable and safe link between the surgeon and the patient.
- High-speed data transmission for real-time feedback.
- 9-degrees-of-freedom for maximum dexterity.
- Intuitive controls that mimic a surgeon’s hands.
The Technical Setup for Remote Surgery
A successful tele-surgery involves a strong technical infrastructure to conduct the operation. The Robendy system links the surgeon in the operating room to the robotic arms by using a secure network that links the robotic surgeon to the surgeon. The data and video are sent with a minimum of latency, and this ensures that there is a real-time connection. The system has redundant communication lines, which would ensure that there are no disruptions. The engineering is such that it makes such a delicate procedure possible.
Enhancing Hospital Capabilities
When hospitals invest in advanced surgical technology such as the robot manufactured by Robendy, it gives them a competitive edge. They can recruit and retain the best surgical talent and increase the number of services they provide. The hospital that has the power of tele-surgery can position itself as the pioneer of innovative care. The technology enables smaller institutions to provide specialized procedures without necessarily having a full-time specialist present.
The Patient’s Experience and Beyond
The end beneficiary of tele-surgery and remote operation is the patient. They no longer need to travel to a distant city to receive specialized medical care. This helps to lessen the burden of the financial and emotional load of patients and their families. The robot also gives rise to improved surgical results because of its accuracy. It is a key factor in improving the overall patient journey from diagnosis to full recovery.
A Case Study in Expanding Reach
An actual case study about the influence of Robendy occurred during its early sales in some other countries. The surgeons took advantage of the abilities that the robot held to treat patients who would otherwise have to travel great distances to get care. The technology had been successful in diverse environments, both in big-city hospital settings and in more distant clinics. The successful operation proved that the robot could be successfully and reliably operated anywhere.
The Future of Robotics and Rural Care
Tele-surgery and remote operation are potential interventions that can be very useful in rural and underserved regions. It makes sure that every patient, no matter what their gender or race may be, is well taken care of by giving them the best medical care possible. Surgeon training in these fields can also be conducted through technology. It offers an opportunity through which trained surgeons can teach and coach others in real time. It is a revolution in medical education.
Reducing Costs for the Healthcare System
The cost argument is frequently part and parcel of the robotics vs. traditional surgery debate. Tele-surgery may save the total expenses of traveling and staying for patients in a distant city. It may also make hospitals less dependent on full-time specialists to perform all possible procedures. The technology offers an affordable means of delivering quality care. The Canadian healthcare system is smart to make such an investment.
Building Trust with Innovation
Both patients and healthcare providers should have confidence in this new technology. The international patent and proven track record demonstrate the commitment to quality and safety by Robendy. The stability and accuracy of the technology instill trust in the system. This trust is core to the successful transition between Robotics and Traditional Surgery. Robendy is committed to playing a dependable role in this medical revolution.
Closing Thoughts
Remote operation and tele-surgery are quickly taking root in the future of Canadian healthcare. The fact that the robot Robendy can cross geographical boundaries is an important step towards achieving fair access to care. Its surgical robot with high-precision that has a high degree of control offers a safe and efficient platform to undertake remote surgeries. This is not only a technological achievement, but a human one.
Conclusion
The Robendy surgical robot is an industry leader in tele-surgery and remote operation. Its modern surgical technology is already demonstrating its worth with its experience in Iran and its potential within Canadian healthcare. The benefits of minimally invasive surgery are clear for patients, and the ability to bridge geographical gaps makes it an invaluable asset. Robendy’s commitment to providing a top-tier tool positions it as a key player in this medical revolution.